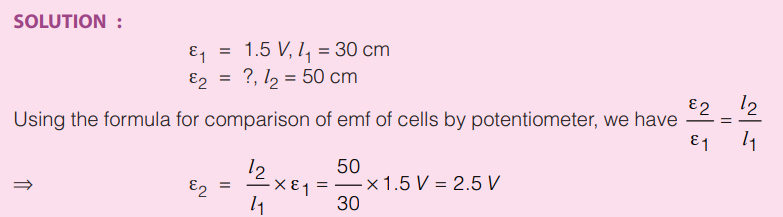Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a conductor of uniform cross-section with a steady current set up in it. This maintains a uniform potential gradient along the length of the wire. Any potential difference which is less than the potential difference maintained across the potentiometer wire can be measured using this.
The wire should have high resistivity and low expansion coefficient.
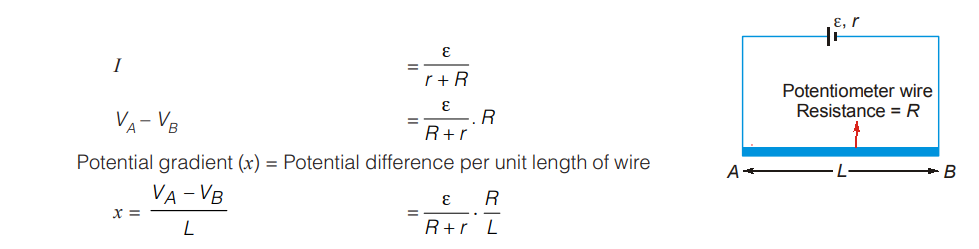
Application of Potentiometer
I.Finding EMF of unknown cell and compare EMF of two cells.
In case I when (2) is joint to (1) then balance length = l1
ε1 = xl1
In case II, when (2) is joint to (3) then balance length = l2
ε2 = xl2
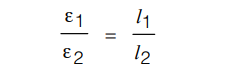
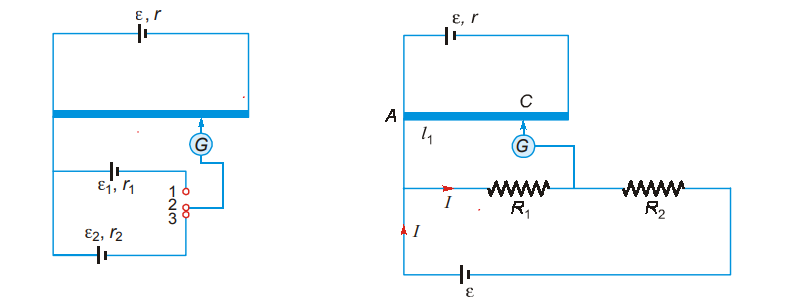
If any one of ε1 or ε2 is known the other can be found. If x is known then both ε1 and ε2 can be found II.
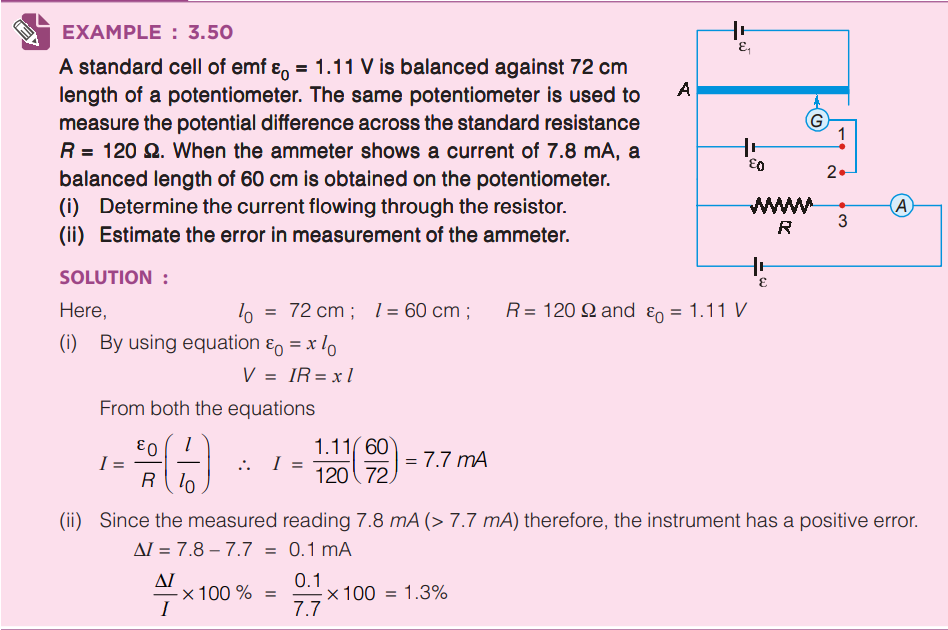
II. To find current if resistance is known
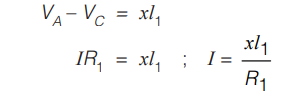
Similarly, we can find the value of R2 also. Potentiometer is ideal voltmeter because it does not draw any current from circuit, at the balance point.
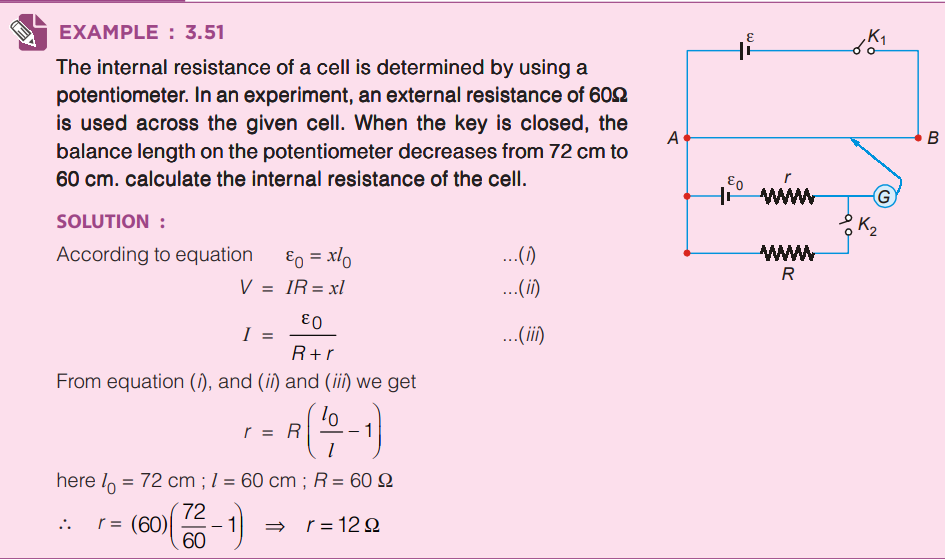
III. To find the internal resistance of cell
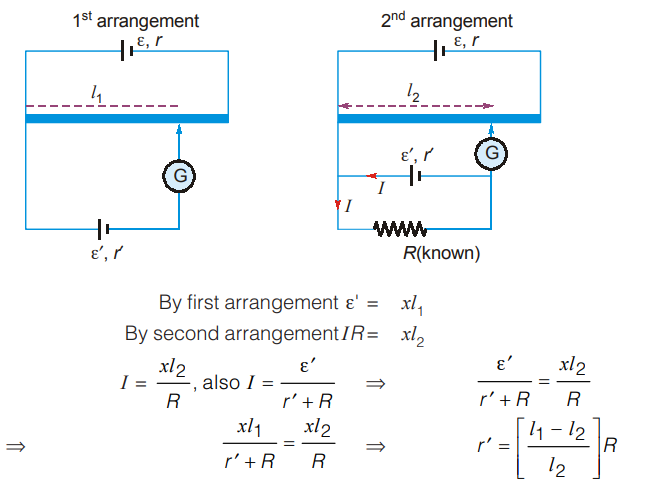
Example :
In a potentiometer arrangement a cell of emf 1.5 V gives a balance point at 30 cm length of wire. Now, when the cell is replaced by another cell, the balance point shifts to 50 cm. What is the emf of second cell?