Lipids
Lipids are formed of Carbon, Hydrogen and often Oxygen where Oxygen content is very small as compared to other two elements.
Lipids do not form polymers in nature except cutin (polymere of fatty acids). Some lipids also contain small amounts of phosphorus, nitrogen and rarely sulphur. Most lipids are formed of fatty acids. In animals fats are present in sub cutaneous layer and work as food reservoir and shock absorber. Lipids require more oxygen for their complete oxidation as compared to carbohydrates but produces double the energy in its comparison.
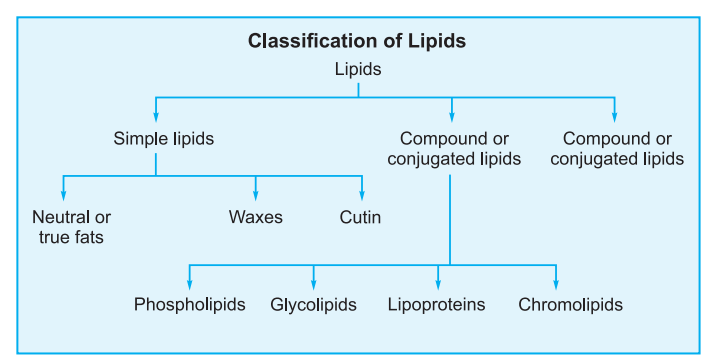
A. Simple Lipids
They are lipids formed of fatty acids and alcohol without any additional group.
e.g. fats or true fats, wax like cutin, suberin. They are of two types:
(a) Neutral fats and oils (b) Waxes
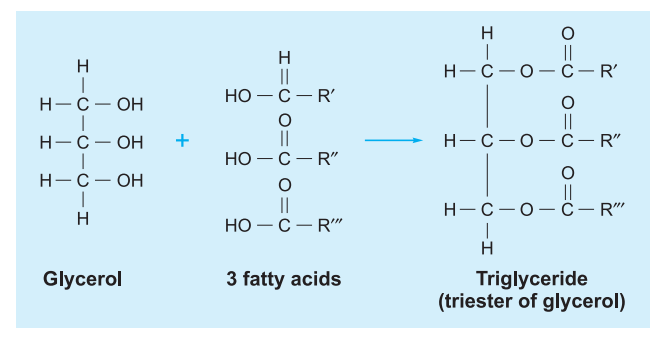
I Neutral Fats: They are esters of three molecules of fatty acids and one molecule of glycerol. Hence, they are also called triglycerides. Two components explained in brief are as follows:
- Glycerol/ Trihydroxy propane: Molecule with 3carbon each bearing a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
CH2 — OH | CH — OH | CH2 — OH
- Fatty acids: These are chains of hydrocarbons which end in carboxylic group. Length of hydrocarbon part of fatty acid is 4-24 carbons. Greasy and insoluble nature of fats and oils is due to structure and length of fatty acids.
Triglycerides: formed by ester linkage of glycerol with the three molecules of fatty acids.
Ester is formed due to reaction between carboxylic group of an organic acid and hydroxyl group of an alcohol removing a water molecule and producing an ester linkage.
- II Waxes: They are esters of long chain fatty acids with long chain monohydric alcohol like ceryl, acetyl or mericyl, e.g., bee’s wax, sebum, spermaceti (from Whale), lanolin (wool fat), plant waxes.
Wax present in blood is cholesterol palmitate. Wax is generally soft and pliable when warm and hard when cold. It is water resistant and function in natural water-proofing of feathers, fur, human skin, insect exoskeleton, leaves and fruits.
B. Conjugated Lipids
These consists of lipids & non–lipid parts. These are of following types –
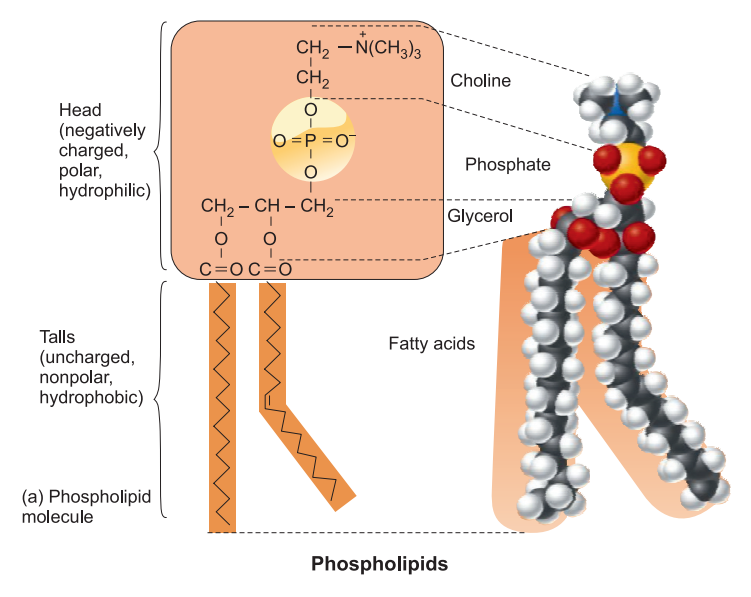
- Phospholipids: Phospholipids are esters of fatty acids with glycerol where one fatty acid is replaced by a phosphoric acid residue (phosphatidic acid) esterified with non nitrogenous or nitrogen containing base like choline and ethanolamine.
EXAMPLES: Lecithin is choline containing phospholipid while cephalin possesses ethanolamine. Phospholipids are major structural components of cell membranes. They are, therefore, also called membrane lipids.
Phosphoric acid and nitrogen containing base functions as polar hydrophilic head while the two fatty acids behave as hydrophobic nonpolar tails.
- Glycolipids: One fatty acid is replaced by sugar, e.g., myelin sheath of nerve fibres, chloroplast membrane. Two common glycolipids are cerebrosides and gangliosides.
- Lipoprotein: They are complex biomolecules formed of Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Cholesterol and Proteins. Lipoproteins are of four types: Chylomicrons, High density lipoproteins (HDL) Low density lipoprotein (LDL) Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL). Membranes are also lipoprotein structure. Lipids are transported in blood plasma and lymph in the form of lipoproteins.
- Chromolipids: Formed by lipid & pigment, e.g.. carotene, xanthophyll. Lycopene present in tomato & red chilli. Carrot is rich in β–carotene, converted into vitamin A.
C. Derived Lipids
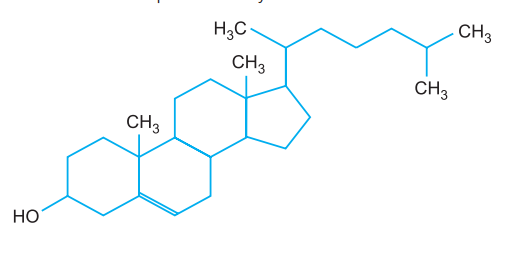
They are derivatives of lipids or lipid-like substances. e.g., steroids and sterols like cholesterol, lipid soluble vitamins, lipids soluble hormones, terpenes, prostaglandins.
- Sterols (Steroids) are crystallisable lipids having four hydrocarbon rings (three cyclohexane and one cyclopentane) and a long hydrocarbon side chain. Fatty acids are absent. Sterols are precursors of steroid hormones and vitamin D. They are essential for plant growth and flowering. The most common sterol is Cholesterol. Cholesterol forms bile salts and hence essential for absorption of fatty acids. It forms vitamin D on exposure to sunlight. In excess cholesterol forms gall stones. It is also deposited in the walls of blood vessels causing atherosclerosis. Cholesterol is constituent and strengthening agent in the membranes of animal cells and mycoplasmas. Ergasterol is a sterol present in fungal cells membranes. Plant cell membranes instead possess stigmasterol. Steroid hormones include progesterone, testosterone, cortisol, and estradiol. Most steroids are anabolic stimulants.