Nucleic Acids
Edited By:
MENIIT Team
| Updated on
Jul 13, 2024 09:55 AM GMT+0000
| #
Zoology
Nucleic acids are linear mixed polymers of nucleotides and are, therefore, also called polynucleotides. They are formed of C, H, O, N and P. Nucleic acids are of two types, DNA and RNA. RNA differs from the DNA as the former contains ribose sugar and all other bases except Thymine while later contains deoxyribose sugar and all other bases except uracil.
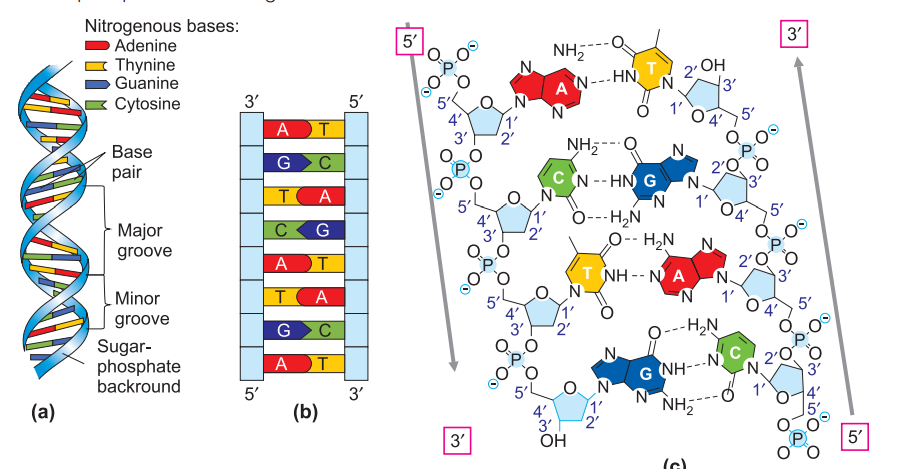
DNA: Structure of DNA was deciphered by Watson and Crick (1953) on the basis of X-ray diffraction pictures obtained by Wilkins, Astbury and Franklin (1953). Wilkins, Watson and Crick were – awarded Nobel Prize for this in 1962. DNA duplex of Watson and Crick is right handed and is called B-DNA.
- Deoxyribose nucleic acid is double helically coiled macromolecule which is made up of two antiparallel poly deoxyribonucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds.
- The two strands are not coiled upon each other but the double strand is coiled upon itself around a common axis like spiral staircase with the base pairs forming the steps while backbone forms the railing.
- The direction of the two strands is 3′ → 5′ in one chain and 5′ → 3′ in the other depending upon the free carbon atom of deoxyribose sugar present at the polynucleotide ends.
- Each polynucleotide strand consist of a sequence of nucleotides linked together by phosphodiester linkage.