Nucleotides
Nucleotides forms the monomer of nucleic acids i.e. DNA and RNA. A nucleotide is composed of three components:
(A) A phosphate group
(B) Pentose sugar
(C) Nitrogenous bases
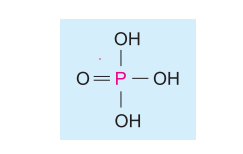
(A) Phosphate group
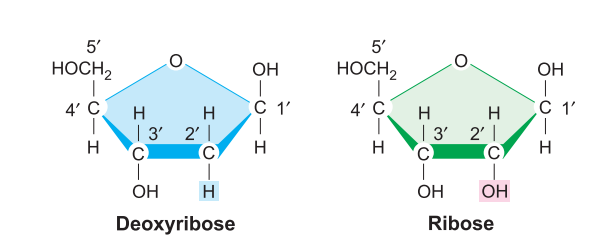
(B) Pentose sugar: RNA has ribose as base sugar while DNA shows the presence of Deoxyribose.
(C) Nitrogenous bases : They are of two types, purines and pyrimidines.
Purines are 9-membered double ring, nitrogen bases which posses nitrogen at 1, 3, 7 and 9 positions, e.g. adenine (A), guanine (G).
Pyrimidines are 6-membered nitrogen bases that contain nitrogen at 1 and 3 positions, e.g., Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), Uracil (U).
Nucleoside
They are compounds formed from a nitrogen base and pentose sugar. Nitrogen base combines with pentose sugar molecule at its carbon atom 1′ in a N-glycosidic bond (C–N–C) by one of its nitrogen atom (1 in pyrimidines and 9 in purines).
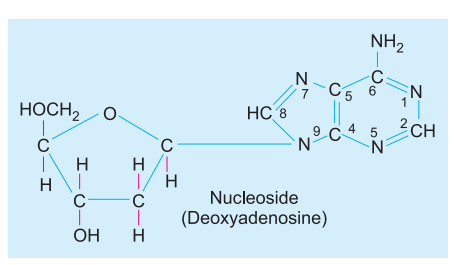
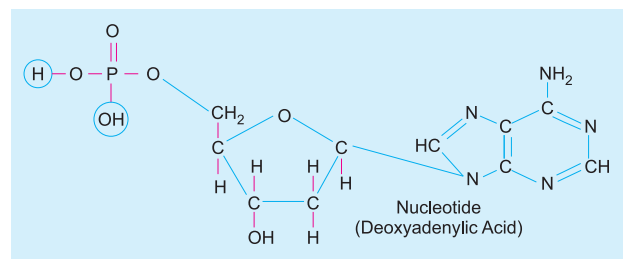
Nucleotide
A nucleotide is a compound made of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar and phosphate, Phosphate combines with sugar at its 5′ carbon with ester bond, sugar with nitrogen base at carbon 1 while nitrogen base is usually attached to sugar at its 9 (purine) or 1 (pyrimidine) atom.